Have you considered Flex or Flex-Rigid PCBs?
Some of the advantage of this technology and associated design considerations
Flexible and Rigid-Flex boards offer many different connection capabilities than standard PCBs which can greatly help to reduce packaging requirements. Other benefits include weight reduction, higher signal speeds, increased reliability in high vibration or harsh environments and reduced cost opportunities. These features help electronics designers solve design issues that would be presented with a standard rigid PCB.
One of the biggest advantages of Flexible and Rigid-Flex boards is they circuits can be designed to fit the available space rather than having to design the size of the product to fit the PCBs.
Detailed below are some of the main advantages of why engineers choose Flexible and Rigid-Flex boards.
Condensed packing requirements, packaging size
- Boards can be folded to use all the available space
- On average a Flex will use 10% of the space of rigid boards
- Large connectors are not needed, saving space
- 3D packaging geometries can be followed allowing further reduction in packaging space needed
- Can replace multiple PCBs, wiring and connectors with one Flex or Rigid-Flex assembly
Increased reliability
- Polyamides are very thermally stable enabling Flex circuits to perform well at high temperatures
- The ductility of Flex circuits means they are an excellent solution for products exposed to high shocks and vibrations
- The need for traditional connectors can be removed thus increasing reliability re assembly issues and connector failures
Reduced weight
- On average a Flex solution will weigh 10% of the same design on a rigid board
- Lower weight circuits reduce overall weight of the product
- The reduction in weight improves the product’s drop test performance
High-Speed signal performance
- Reduced track and gaps width for high density designs because:
- Material thicknesses with tight tolerances provide very consistent impedance values
- Flex material have low DK values, typically from 3.2 to 3.4
- Homogeneous
Resistant to harsh environments
- Impermeable to moisture
- Resistance to solvents, oils ad acids
- Fire standard UL94V-0 approval
- Good performance over a wide temperature range (-200°C to 400°C)
- Compared to other dielectric materials Flex has higher heat dissipation
- Polyamides have minimal expansion and contraction
- Resistance to UV exposure
- High dielectric holding voltage, > 3KV
Lower cost
- Simplified, faster assembly process results is less labour costs
- Less assembly failures with fewer connectors
- Reduced packaging requirements reduces the size of the finished assembly
- Smaller assembly reduces the amount of materials and therefore cost
Connector and component and compatibility
- Simplified, faster assembly process results is less labour costs
- Accepts any component or connector that can be assembled on a rigid PCB design
- Possibilities include PTH, High-Density BGA and High-Density SMT
- Direct soldering possible
Design Considerations
Corners with flexible bending areas
Acceptable Design

Acceptable Design

Unacceptable
Staggered track positioning from layer to layer
Staggering the track placement on each layer eliminates the "I-Beam" effect that improves the flexibility and reliability of the circuit.
Avoid vias in bending arears
It is not recommended that vias are placed in areas of the boards that will bent as this will add stress and can cause breakages.
Stiffener termination and Coverlays
Proper reinforcements and roofing terminations prevent significant areas of stress with the flex circuit.
Different types of Flex circuits
Single Sided Flex
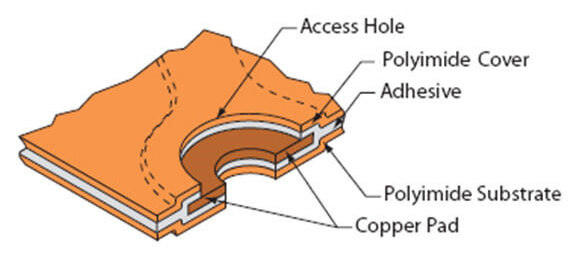
Double Sided Flex
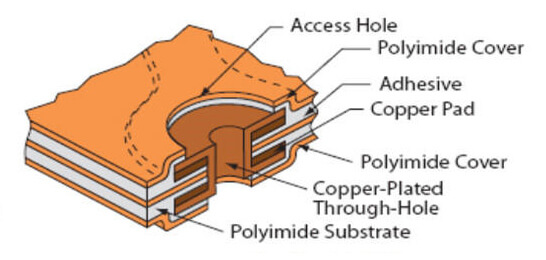
Multi-layer Flex
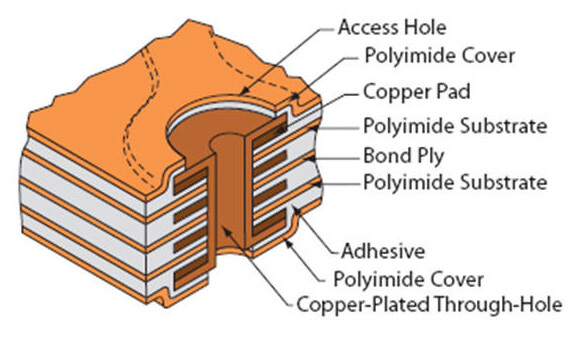
Rigid-Flex
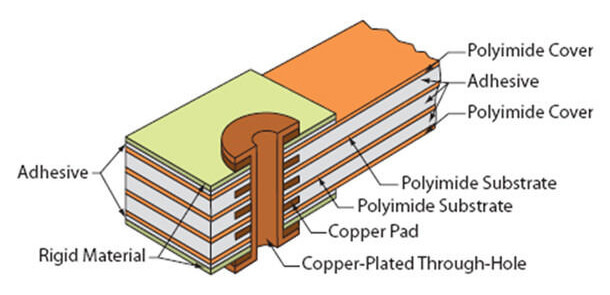
Common Flex material Stack-Up
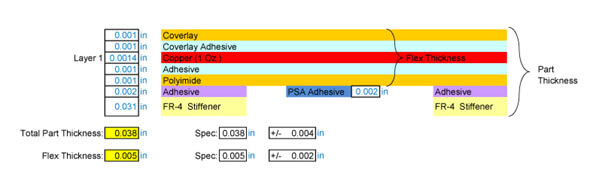
Single layer Flex PCB with optional FR-4 stiffeners and PSA
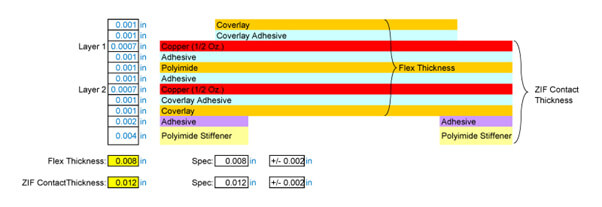
Flexible 2 layer circuit with ZIF contact fingers
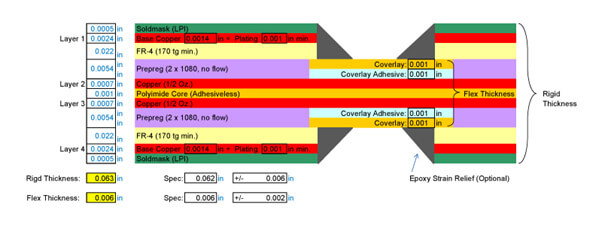
4 Layer Flexible Rigid PCB (2 Flexible Layers)
Date : 05-01-2022